|
🔎Photo source: www.kristenallott.com
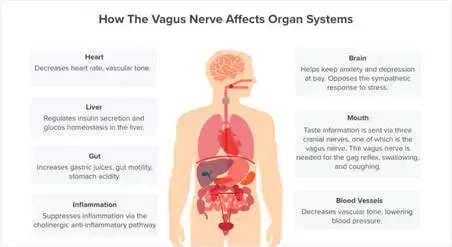
🔎The Vagus Nerve is the longest and most complex of the cranial nerves. Vagus means “wanderer”. ⬇️It travels from the brain stem down to the abdomen and connects with many major organs participating in many of our bodily functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate and many more. It is closely connected to the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and therefore plays a big role in regulating stress responses 💥 🏵️The ANS runs our bodies automatically without us being aware of it🏵️ The ANS has 2️⃣ branches, the sympathetic and the parasympathetic, and responds to signals and sensations via three pathways, each one with a characteristic pattern of response. ✳️The working principle of the ANS is “every response is an action in service of survival”✳️ The ANS acts to manage risk and seek safety. These actions are automatic and adaptative, generated well below the level of conscious awareness. 🔹The sympathetic branch is situated in the middle part of the spinal cord and prepares us for action. It responds to cues of danger and triggers the fight or flight response. 🔹The parasympathetic branch has two pathways traveling within the vagus nerve. 👉Ventral vagal pathway: responds to cues of safety and supports feelings of being safely engaged and socially connected 👉Dorsal vagal pathway: responds to cues of extreme danger. It takes us out of connection, awareness and lead us into a protective state of collapse This is the freeze response. 🔎Polyvagal theory helps us understand that both branches of the vagus nerve calm the body, but they do so in different ways. 👉Fight or flight response of the sympathetic branch releases adrenaline and prepares our body to action by mobilizing the muscles, dilating the pupils, increasing the sweating, accelerating the heart rate, enhancing the senses, etc. 👉Shutdown or freeze, occurs through the dorsal branch of the vagus nerve. This reaction can feel like the fatigued muscles and lightheadedness of a bad flu. In addition to affecting the heart and lungs, the dorsal branch affects body functioning below the diaphragm. Check more here.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorHi there! Archives
January 2022
Categories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
